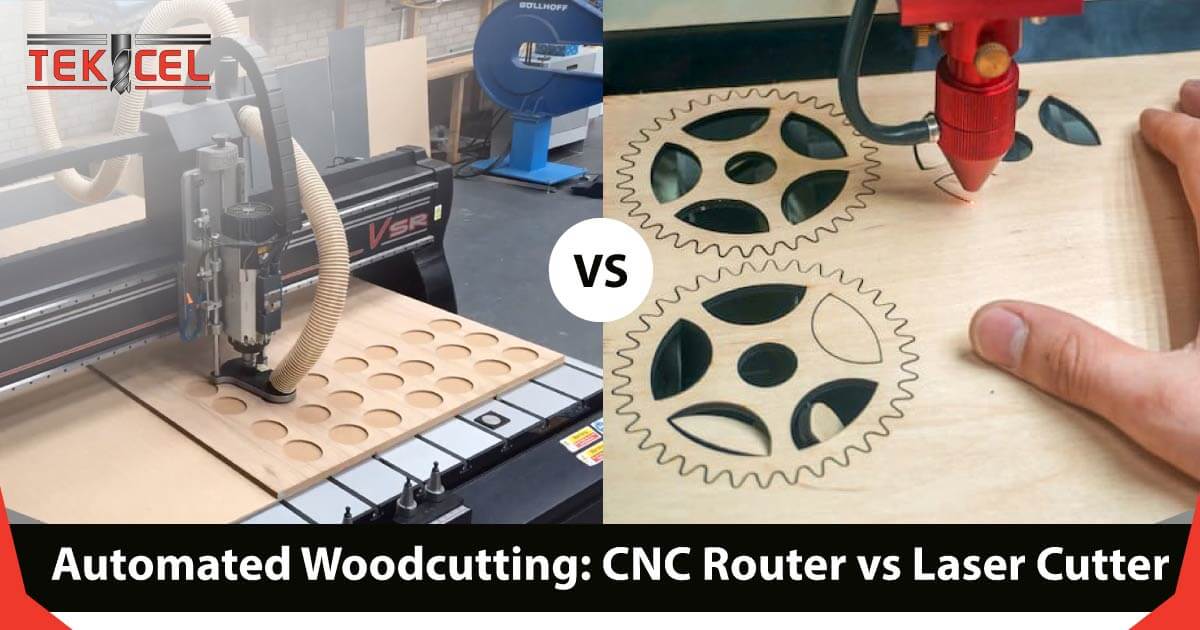

When it comes to cutting wood machines, there are two popular options: a CNC router and a laser cutter. Both have their own strengths and weaknesses.
The CNC router uses a spinning tool to cut through wood, making it ideal for tasks like carving and engraving. On the other hand, a laser cutter uses highly focused light to cut. It can quickly and cleanly cut through materials such as wood and plastic.
So which should you choose? It really depends on your project and specific requirements. If you need detailed engraving or sculptures, a CNC router may be the way to go. However, if speed and precision are your top priorities, a laser cutter could be more suitable.
Regardless of which option you choose, automated woodcutting technology can provide numerous benefits in the workshop. It can greatly increase efficiency and precision in making wood products.
But with so many options on the market, it can be difficult to know which automated woodcutting machine is best for your needs.
Here are some of the considerations you should factor in when making your decision.
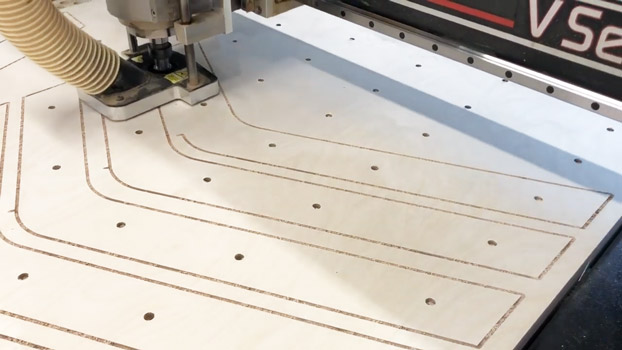
A CNC router uses a rotating cutting tool to carve out shapes in wood or other materials. The result is precise and clean cut. However, this process can be time-consuming and may require multiple passes for thicker pieces of wood.
In contrast, a laser cutter uses a focused beam of light to quickly cut through thin wood. Laser cutting has more precision and better accuracy. However, the material must be placed precisely within the laser’s field in order to get an accurate cut. Making it more challenging to work with larger or irregularly shaped pieces.
Overall, both methods have their place in the woodcutting process. Ultimately it comes down to personal preference or project requirements. Each has its own unique capabilities and can produce beautiful results with the right application.
One key difference is the depth of cuts they can make.
A CNC router typically has a much deeper cutting capacity. As it uses a rotating blade to cut into the material.
On the other hand, a laser cutter uses focused light to melt or vaporise the material. It results in shallower cuts but with smoother edges.
So when deciding between these two tools, it’s important to consider not only the type of material you’ll be cutting but also the desired depth of your cuts.
In cases where deep cuts are required, a CNC router may be the better option. However, for projects that require precise and smooth edges, a laser cutter may be the way to go.
Ultimately, both are useful tools in any maker’s toolkit.

wood laser cutting
CNC routers use rotating blades to cut material, making them well-suited for tasks such as carving and routing. Laser cutters, on the other hand, use focused beams of light to melt or burn through material, allowing for finer details and a smoother finish on projects.
Ultimately, the best option will depend on the specific needs of your project. You can decide how much millimetre precision you need for the cut.
When it comes to completing certain tasks in a manufacturing setting, both CNC routers and laser cutters have their own unique advantages.
In terms of labour effort, a CNC router may require more physical work to operate. As the materials must be loaded and secured onto the machine manually. However, a CNC router can also handle a wider range of materials and has the ability to drill as well as cut.
Laser cutters, on the other hand, often require less physical labour. As they can easily switch between different materials and have a smaller footprint.
Additionally, laser cutting produces less noise and waste compared to the router alternative. Ultimately, the decision between the two technologies largely depends on the specific task at hand and the availability of resources.
cnc woodcutting

cnc router woodcutting precision
When it comes to energy consumption and cost, there are some key differences between CNC routers and laser cutters.
CNC routers have high starting costs, but they typically use less energy over time. They have the ability to run continuously without stopping for cooldown periods.
Laser cutters, on the other hand, have lower starting costs but require frequent cool down periods that eat up energy and increase operating expenses.
Of course, budget and practicality may also play a role in choosing between the two. While laser cutters often have a higher upfront cost, they also tend to require less maintenance over time. Factoring in energy usage can help ensure cost-effective and sustainable operations in the long run.
It’s important to consider both the initial cost and long-term energy consumption when weighing your options for a cutting machine.
CNC router vs laser cutter. The best option will depend on the specific needs of your business or project.
When it comes to choosing the right equipment for your project, can sometimes be a difficult decision. Should you go with a CNC router or a laser cutter? Both have their own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice will depend on the specific needs of your project.
That’s where Tekcel comes in with the best CNC router in the industry.
Our knowledgeable team can provide you with all the necessary information to help make the best decision for your project. We can also offer support and guidance in using whichever equipment you choose. We ensure you get the most out of your investment.
Don’t hesitate to contact us for more information on CNC routers. We’re here to help.